APPLICATIONS
Industrial & Commercial Heating Uses
- Workshops
- Warehouses
- Supermarkets
- Offices,
- Gymnasiums
- Schools
- Exhibition halls
- Drying process such as food and painting.
Agricultural Heating Uses
- Greenhouses
- Poultry houses (see agricultural KWIH series)
ADVANTAGES
- Decentralized and oriented heating.
- Simple installation and operation.
- Wide power range from 50,000 Btu/hr to 400,000 Btu/hr or 15kW to 117kW.
- Quick solution for heating large spaces, warehouses and garages.
- No need for a heat distribution network.
- Simple to control with a thermostat.
- High efficiency achieved by condensing units.
- Easy maintenance.
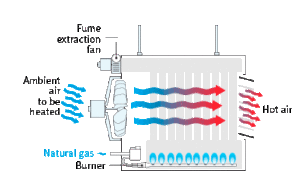
HOW IT WORKS
A unit heater is a stand-alone appliance serving to heat a given space and capable of operating on propane or natural gas.
The equipment usually includes a heat exchanger, through which a fan blows air from the room to be heated. There are two types of indirect-fired heaters, indirect-fired axial heaters (WAB) and indirect-fired centrifugal heaters (WCB). The temperature rise is about 28°C and 36°C, respectively. The air flows and the blowing distances are much greater with a centrifugal fan, and sometimes designed with a duct to distribute the warm air.

- Natural gas or LPG.
- Rates 50/80/150/200/300/400 x1,000 Btu/hr or 15/23/44/58/88/117kW
- Inshot burner makes the combustion more complete with lower CO and NOx.
- Heat exchanger made by aluminized steel or stainless steel pipes.
- Reliable Direct Spark Ignition.
- The 12VAC low-voltage ignition controller, specially developed for HVAC industry, all troubleshoots can be easily identified by the indicator lights
- Safer and reliable low-voltage 24 VAC combination gas valve with 100% shut off.
- Flameout protection, fan malfunction protection, and overheating protection.
- Special baffles in the heat exchanger can enhance the heat exchange efficiency.
Heating Power:
Warehouse: 25-35 Btu/hr per ft2 or 80-110 W/sqm
Mechanical workshop: 40-60 Btu/h per ft2 or 120-180 W/sqm
Here are the criteria to consider in selecting the units:
- Installation height;
- Positioning;
- Axial fan or centrifugal blower
- Heating power;
- Combustion: sealed or unsealed combustion;
- Venting: combustion products are usually vented outdoors.
It is always best to start with a pre-installation checklist; a list of things to check before an installation takes place. The following is a basic checklist and is meant to serve as an example:
- Pick a location that is suitable for the unit that is being installed.
- Make sure that venting requirements can be met.
- Check for structural issues that may affect the installation of piping or duct work.
- Plan a gas piping route, including pipe sizing, that will properly supply the system.
- Plan for proper condensate drainage when applicable.
- Check for the proper clearance to combustibles as recommended by the manufacturer and in accordance with local codes.
- Make sure the installation will leave the unit accessible for future service.

